How does a normal heart beat?
Heart muscle cells are activated by electrical impulses that cause them to contract regularly and in sync. This contraction produces a heartbeat, allowing blood to be pumped out to the entire body.
Electrical impulses originate from specialized cells called the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is the heart’s natural pacemaker.
The SA node is located in the upper right chamber of the heart, the right atrium. From the SA node, the impulse spreads across the upper chambers of the heart to reach the atrial-ventricular (AV) node located between the atria and lower ventricles. After leaving the AV node, impulses spread across the pumping chambers of the heart, the ventricles.
As impulses are spread along the heart, the cardiac muscle cells are stimulated to contract, producing a heartbeat.
Animation of How a Normal Heart Beats
Arrhythmias
Conditions in which the heart beats with an irregular or abnormal rhythm. Some arrhythmias occur without symptom while others have symptoms of increasing severity.
Understanding normal electrical conduction through the heart
Causes of Arrhythmias
Disease, injury or any condition that disrupts normal conduction or creates a lack of oxygen to the heart tissue cells responsible for heart rate. Excessive physical and mental stress. Alcohol and drug abuse may also be a factor to consider in causes of some arrhythmias
Common Symptoms
Include, but not limited to, palpitations, chest tightness or peain, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, fainting or black-out, fatigue, exercise intolerance and excessively slow or fast heart rates, Symptoms may be constant, persist frequently or be infrequent and random which may require patient to be monitored to catch the moments when symptoms appear, This may be done with a Holter or Event monitor, or an implanted event recorder to capture the specific arrhythmia with it happens to confirm diagnosis.
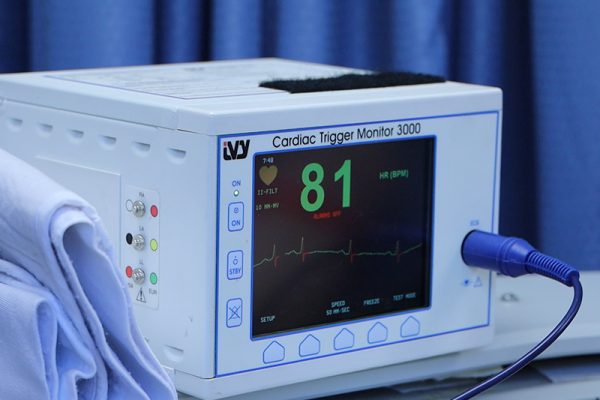
EKG
The electrocardiogram is used to measure conduction through the heart and help identify any aberrancy.