Procedures
There is an epidemic of atrial fibrillation and may reduce quality of life, increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and even death. Atrial fibrillation results in adverse atrial remodeling and eventually leads to persistence of atrial fibrillation making it more difficult over time. Catheter ablation has evolved to be a safe procedure in experienced centers, but we need to do it carefully.
Ablation is the use of heat to vaporize abnormal tissue or restore normal functioning. Catheter ablation is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube is inserted into a vein in the upper thigh and threaded through the bloodstream to the abnormal area. In cardiac care, the catheter is guided to the heart where radiofrequency energy (radio waves) is applied through the catheter. Catheter ablation is most often used in cardiac care to treat atrial fibrillation and some other types of arrhythmia or heart rhythm disorders.
A catheterization, also called an angiogram is an invasive procedure that allows Dr. Jamnadas to evaluate the hearts function. A cardiac catheterization is used to determine the presence of heart structural defects, coronary artery disease, valvular disease, or disease of the aorta. This can show whether further cardiac treatment is needed.
Cardioversion is a procedure used to treat abnormal and rapid heart rhythms known as cardiac arrhythmias. Cardioversion is most commonly used for atrial fibrillation. Cardioversion delivers an electrical ‘shock’ to the heart to restore the heart to its normal rate and rhythm.
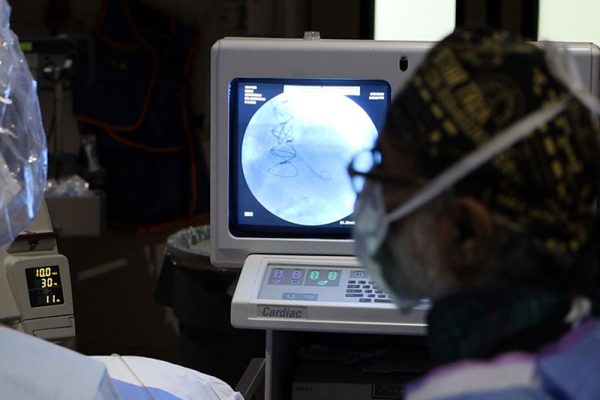
Angioplasty is an invasive procedure used to widen a narrowed or blocked artery in the heart by using a thin catheter with a balloon at the end. The balloon catheter is positioned in the narrowed segment of the artery. Inflation of the balloon causes the balloon to push outward against the blockages and surrounding wall of the artery allowing blood to flow through more easily.
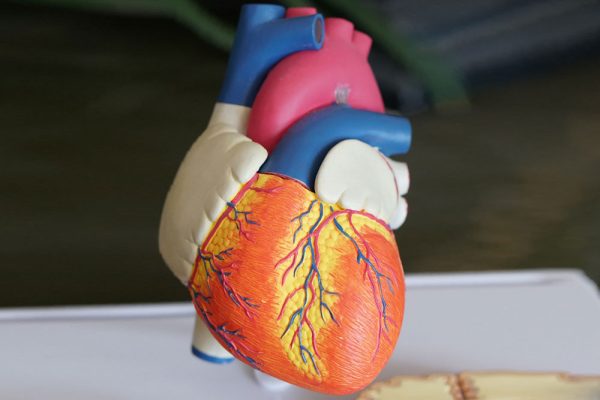
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) is a procedure which takes a blood vessel from a part of the body to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. CABG is used for patients who have coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD is due to a disease process called atherosclerosis caused an accumulation of cholesterol, protein, calcium, etc. Collectively, these form what is called plaque within the coronary arteries.

A stent is a mesh wire which acts as a scaffolding to keep an artery open to ensure blood flow. Blockages are due to the formation of fatty plaques known as atherosclerosis. When this plaque ruptures, a clot will form leading to further obstruction of the artery. When this condition affects the vessels of the heart it is called coronary artery disease.
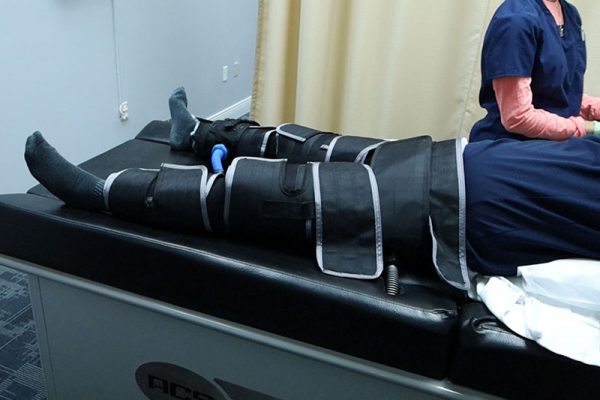

EECP is a non-invasive, FDA approved, outpatient therapy for patients having coronary artery disease with persistent symptoms of angina or heart failure who have already had the standard treatments for revascularization or those who are not eligible for surgical intervention. EECP stimulates the formation of collaterals to help create a natural bypass around narrowed or blocked arteries to improve coronary perfusion.
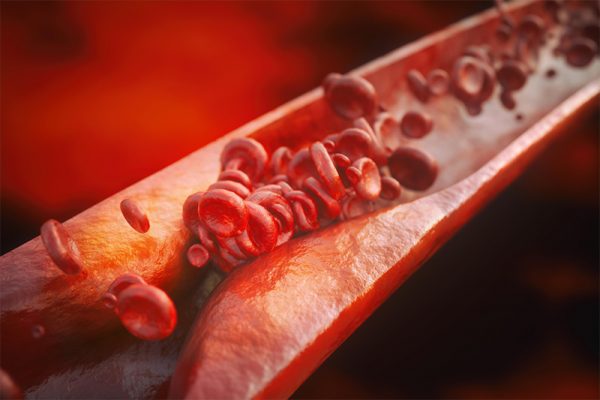
Angioplasty is an invasive procedure used to widen a narrowed or blocked artery using a thin catheter with a balloon at the end. A blocked artery can occur anywhere in the body. Blockages are due to the formation of fatty plaques known as atherosclerosis. When this plaque ruptures, a clot will form leading to further obstruction of the artery. When this occurs in the peripheries it is known as peripheral vascular disease.
