Topics
Research has shown that the consumption of alcohol in moderation reduces the risk factors associated with coronary artery disease. A moderate amount of alcohol refers to an average of one to two drinks per day for men and one drink per day for women.

So, what is an anti‐inflammatory diet? An anti‐inflammatory food is one that is not alien to the body; the body is familiar with this food because it has been in our diet for tens of thousands of years.

Supplement and diet recommendations for patients who have dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinsonism, or any other neurocognitive dysfunction or degenerative disorder.
This list is for information only and includes only the most common medications used in treating cardiovascular disease. You should always speak with your healthcare provider and/ or pharmacist for more detailed information on your medications.

Fish oil is the oil derived from the tissue of oily fish. Fish oil can be obtained from eating fish or by taking fish oil supplements. Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Omega-3 may also be derived from a plant source containing alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of the ability of foods (specifically carbohydrates in food) to raise your blood sugar (glucose) levels after being eaten. The GI scale ranks carbohydrates from 0 to 100, with 0 as the slowest absorption and 100 as the fastest absorption into the bloodstream. Foods with a high GI (above 70) are quickly digested and absorbed, resulting in a rapid increase in blood sugar and, consequently, insulin levels.
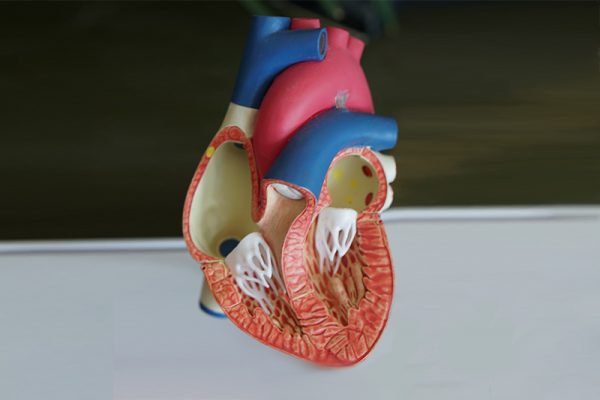
The heart consists of four chambers. The top two chambers (atria) receive blood while the bottom two chambers (ventricles) pump blood out.

Vitamin and mineral supplements combined with an unrefined diet high in fruits and vegetables, some omega-3 oils, no hydrogenated fats, and a good lifestyle are the basics for a healthy heart. Include weight control, not smoking, some exercise, and the ability to manage stress, and you will improve your general health and prevent or help control heart disease.

Although we are living in the 21st century, our human genome is greater than 10,000 years old. The way we metabolize our food is largely determined by our genetic machinery. Yet today, we live in a mechanized urban setting, lead sedentary lifestyles, and eat highly processed and synthetic diets that our genome is not accustomed to.
Physical activity protects against the development of CVD and also improves other CVD risk factors, including high blood pressure, blood lipid levels, insulin resistance, and obesity. Physical activity is also important in the treatment and management of those with hypertension, stable angina, prior myocardial infarction, peripheral vascular disease, or heart failure. Physical activity, therefore, is important for cardiac rehabilitation.
