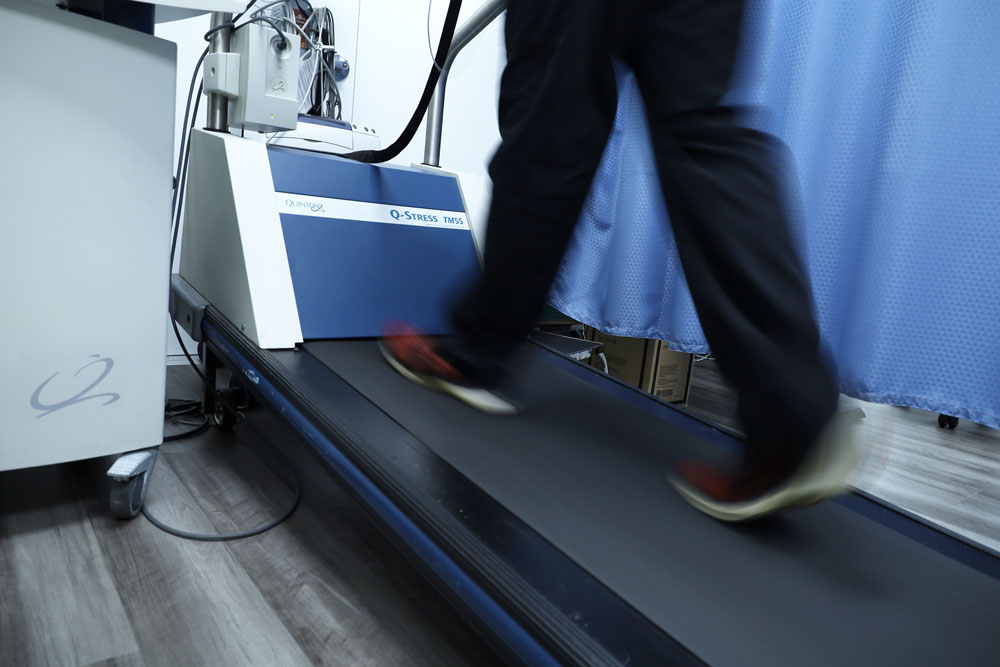
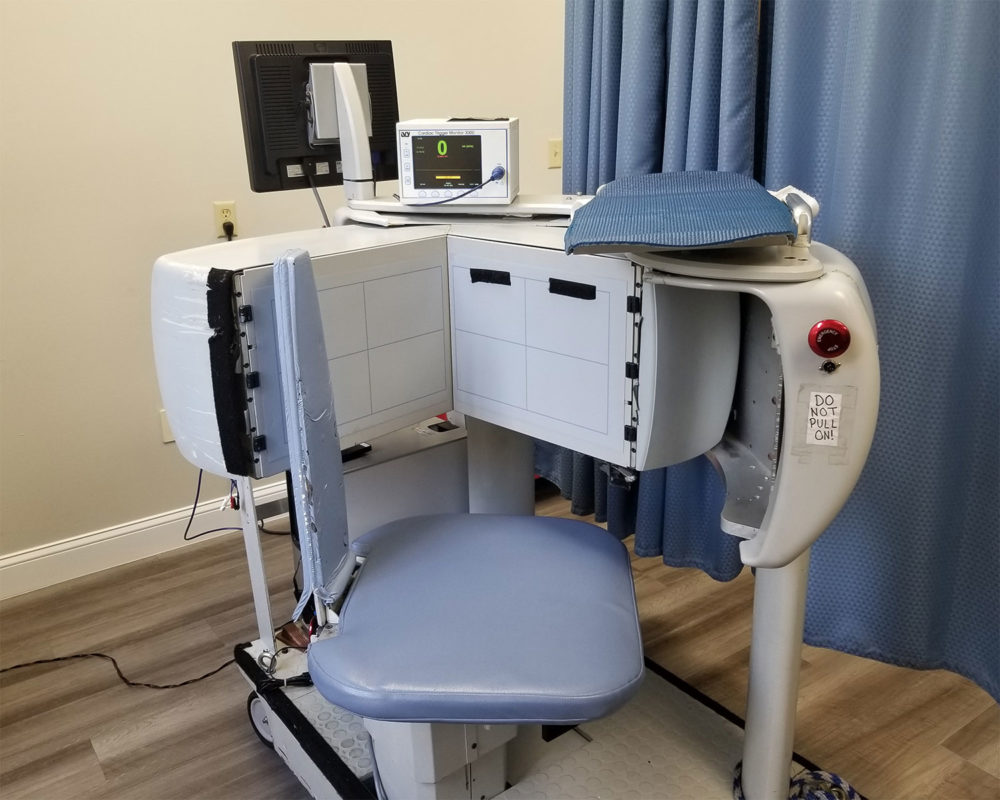
What is a nuclear stress test?
A nuclear stress test is used by cardiologists to diagnose and monitor many heart conditions including coronary artery disease. It measures the blood flow to your heart both at rest and during stress on the heart during exercise.
Resulting images illustrate the amount of blood flow in all sections of the heart, which can show areas of low blood flow and damaged tissue. These sophisticated tests detect the effects of blockages on the myocardium and allows the cardiologist to determine whether the heart muscle is being deprived of blood flow, usually seen with blockages of greater then 70%.
Why do I need a stress test?
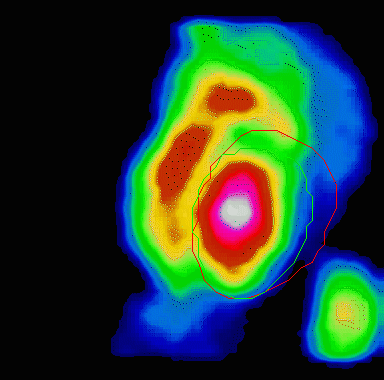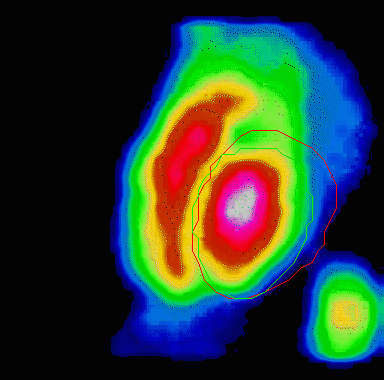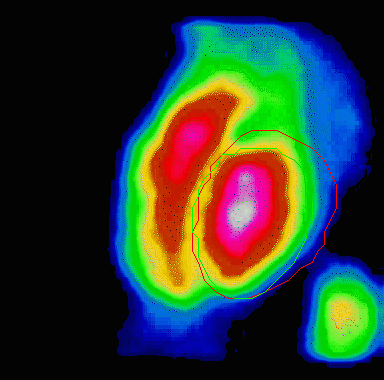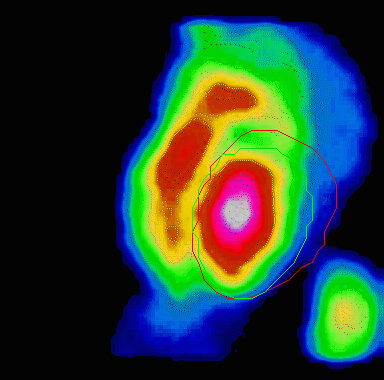
Animation showing a poorly functioning left ventricle
- If the doctor suspects you have coronary artery disease or if you are experiencing symptoms of chest pain or sudden loss of breath.
- To asses the amount of a possible blockage within the vessels of the heart.
- A stress test may be advised to you even if you have already been diagnosed with coronary artery disease to asses the effectiveness of the treatment you are on.
- An accurate stress test Decreases the use of unnecessary stenting.
How do I prepare for the test?
- Wear sneakers and comfortable clothes (preferably a button down shirt with no metal buttons or zipper).
- Avoid wearing long chains and necklaces.
- Continue your medications up to the day of the procedure.
- Stop this medication on the day of the test:
- Beta blockers including: Atenolol, Toprol, Metoprolol, Lopressor, Coreg, Zebeta, Betapace, or Corgard
- If you have asthma and use an inhaler, bring it with you to your test.
- Do Not smoke on the day of the test… or ever!!!
- Do not apply body lotion on the day of the test
- If you need to cancel your appointment, please do so at least 24 hours prior to your test or you may be charged.
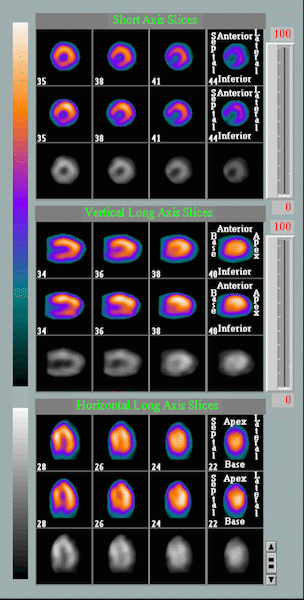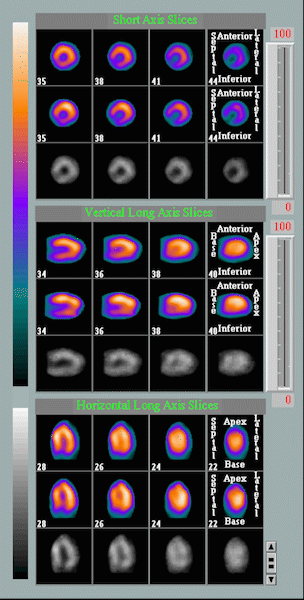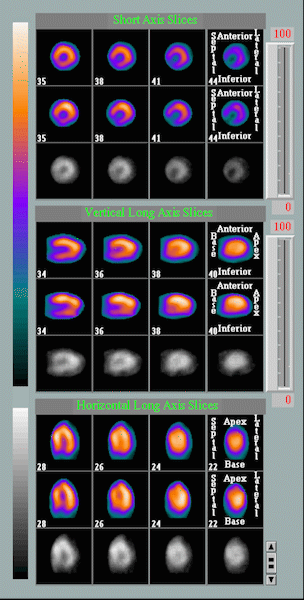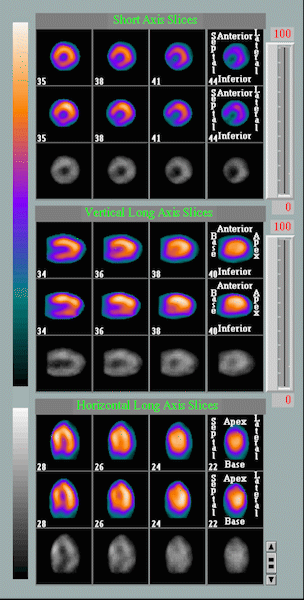
Animation comparing the heart at rest and under stress
What should I expect during the test?
A trained technician will place electrodes on your chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes connect to wires on an electrocardiogram (EKG) machine. The EKG records the electrical activity of the heart.
Next, you will slowly begin walking on the treadmill. As the test progresses, the speed and incline on the treadmill increases. Your blood pressure and EKG will be monitored throughout the test.
The length of the test depends on your physical fitness and symptoms. The goal is to have your heart working hard for about 5- 15 minutes in order to thoroughly monitor its function. Exercise is continued until you reach your target heart rate.
During the test you may develop symptoms or signs of:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- High or low blood pressure
- Abnormal heart rhythm
- Dizziness
You may stop the test at any time if uncomfortable. Symptoms typically disappear once you rest.
The test lasts about 30 minutes.
What are the risks?
Stress tests are generally safe and complications are very rare. Although with any medical procedure, it does carry a small risk of complication.
These complications include:
- Hypotension: blood pressure may fall during or after exercise that can cause dizziness. This will usually ease off once you stop exercising.
- Abnormal heart rhythms may occur during exercise. This usually returns to normal once exercise is ceased.
- Chest pain or flushing feeling may occur
The Result
Once the test is completed, the results of your test will be assessed to determine the condition of your heart. This is useful in planning for your treatment and also helps in determining whether further testing is needed.
A stress test may reveal:
- The results may be beneficial in confirming or ruling out the diagnosis of heart disease
- Confirm whether you are in a stable state
- Assess the development of new blockage
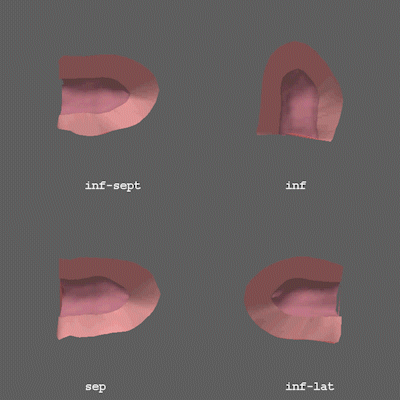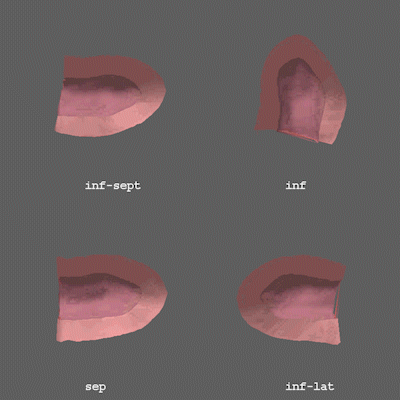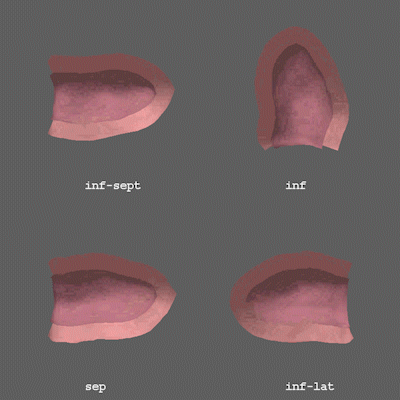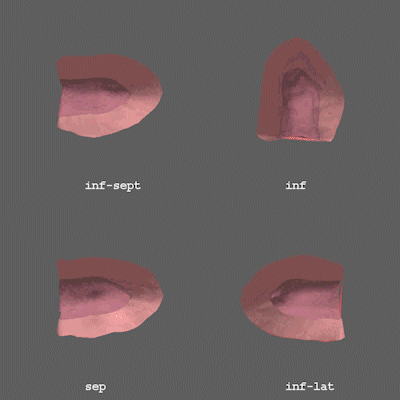
Animation showing the thickness of the heart walls.